By Marc Seltzer; originally published on December 9, 2009, at care2.com
. . .
Should the unused TARP funds go to support middle class job creation or be used to pay down the deficit?
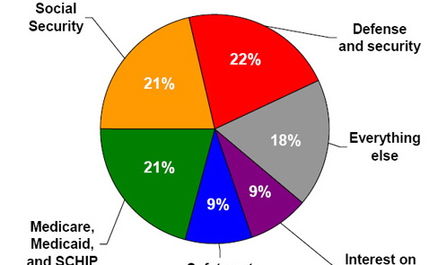
The question has arisen recently after the Treasury reported that its losses on the 350 billion dollars that Congress provided for the administration’s Troubled Assets Relief Program (TARP) are expected to be much lower than originally predicted.
The President and Democratic leaders are calling for a portion of the remaining funds (as much as $200 billiion) to be used for job creation programs. The President has outlined several ideas that the administration believes could help bring unemployment rates down faster than at the current rate of economic recovery:
- Small business financial assistance and tax breaks
- Unemployment benefits, cobra subsidies, and emergency assistence to seniors
- Additional infrastructure and incentives for home energy conservation
However, this money could alternatively be used to pay down the deficit and Republicans are calling for committing all of the funds to deficit reduction.
The PBS Newshour recently featured a brief debate between Princeton Professor and Nobel Laureat economist Paul Krugman and columnist and former Treasury official and Reagan administration advisor Bruce Bartlett on whether President Obama should direct unused TARP funds towards creating jobs or paying down the deficit.
Krugman called for action on the basis that the unemployment rate was devastating and unacceptable. He noted that unemployment was expected to remain far higher than normal in the next two years. Extended unemployment would cause lasting harm to people who were forced to use up their savings and cause long-term damage to future employment prospects, he argued.
Bartlett cautioned that Congress had appropriated the money specifically to help financial institutions under TARP and that it should not be rerouted without congressional approval. While he said he was “agnostic” about the President’s ideas for job creation, he did not support action now because Congress had already enacted substantial stimulus legislation.
Paul Krugman: “And we have what is really an ongoing economic emergency. I mean, this — it’s not just that we’re not creating jobs. The level of unemployment we have got is doing enormous damage. So, I think the president is justified in reaching for whatever mechanism he can.
If — if he can say — you know, it really doesn’t make a difference in terms of the economics, where it’s funded from. If he can say, look, what we’re doing is redirecting funds, and make it happen, then he needs to do it, because, ultimately, what we have is a jobs crisis. Action must be taken. I think the paperwork is relatively less important at this point.”
BRUCE BARTLETT: “Well, I thought, if we were facing the kind of crisis situation that we were when TARP and the original stimulus were enacted, that would be one thing. But I don’t think we’re facing that. I think we have — we did enact the stimulus. The money is — there’s a lot of money still to come from that in the pipeline. I think we have only spent about a fourth of it so far.
The unemployment rate is coming down. I think that there’s a case for, let’s wait a little while. Why not wait until after the president submits his budget in February? Why rush to act this minute?”
With high deficits and high unemployment there are strong competing interests for the money. What do you think is the most important priority at this time?
For a podcast conversation on jobs stimulus between care2.com blogger Jessica Pieklo and myself, follow this link and click on the December 9, 2009, podcast.
Follow me on Twitter